Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that affects millions of people each year. It is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that carry air to and from the lungs. This inflammation can cause coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, among other symptoms. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at bronchitis, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Causes of Bronchitis:
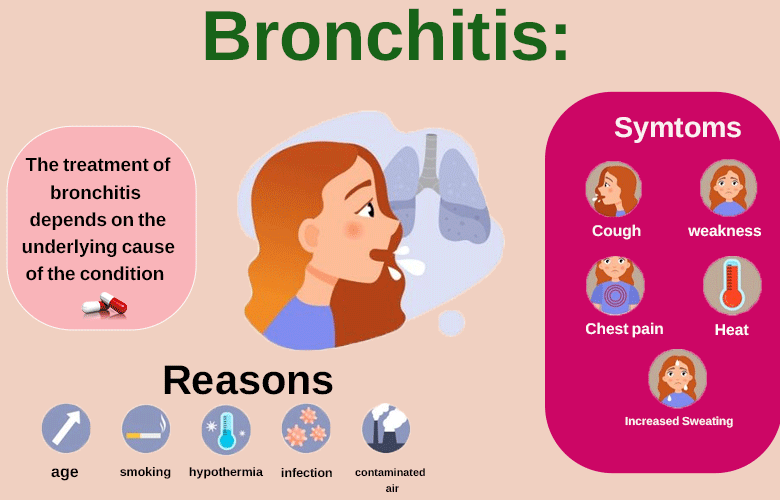
Bronchitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral or bacterial infections, environmental irritants, and allergies. The most common cause of acute bronchitis is a viral infection, such as the common cold or flu. In some cases, acute bronchitis may also be caused by a bacterial infection.
Chronic bronchitis, on the other hand, is often caused by ongoing exposure to irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and workplace chemicals. It is also a common symptom of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is a long-term lung disease that includes both chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
Symptoms of Bronchitis:
The symptoms of bronchitis can vary depending on whether it is acute or chronic, as well as the underlying cause of the condition. However, some common symptoms of bronchitis include:
- Coughing: This may produce mucus or phlegm, and may be worse in the morning or at night.
- Wheezing: This is a high-pitched whistling sound that is made when you breathe.
- Shortness of breath: This may be accompanied by chest tightness or discomfort.
- Fatigue: You may feel tired or weak, especially if your bronchitis is caused by a viral infection.
- Low-grade fever: This is more common with acute bronchitis and may last for a few days.
- Sore throat and nasal congestion: These are less common symptoms of bronchitis, but may be present if your condition is caused by a viral infection.
Treatment of Bronchitis
The treatment of bronchitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. If your bronchitis is caused by a viral infection, you will typically need to rest, drink plenty of fluids, and take over-the-counter medications to relieve your symptoms. Antibiotics are not effective against viral infections, so they are not usually prescribed for acute bronchitis.
If your bronchitis is caused by a bacterial infection, your healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics. It is important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you start feeling better before you finish the medication.
For chronic bronchitis, the focus of treatment is on managing symptoms and preventing further damage to the lungs. This may include quitting smoking, avoiding exposure to irritants such as air pollution and workplace chemicals, and using medications such as inhalers to open up the airways and reduce inflammation.
In some cases, people with chronic bronchitis may need oxygen therapy or pulmonary rehabilitation, which is a program of exercise, breathing techniques, and education to help manage their condition.
Conclusion:
Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that can be caused by a variety of factors. The symptoms of bronchitis can be uncomfortable, but most people recover fully within a few weeks with proper rest and self-care. If you suspect that you have bronchitis, it is important to see a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment. By taking steps to manage your condition, you can reduce your symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.